Coming up with a good business model can feel like an uphill task. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll explain what a business model is and how to make your own, easy as that.
A business model is a document that outlines how your business is going to make money, and setting up this document helps you organize and verbalize your ideas. I
You want a business model to lays out how you’re going to win in an overly saturated markets and generate a substantial income. The business model can be used to pitch your idea to partners, investors, or future employees.
Why does a business model matter?
There are many ways in which a good business model makes a difference:
- Strategy and planning: It helps you plan ahead and make good strategic decisions. You can align your activities, resources, and marketing to reach the goals and KPIs outlined in your business model.
- Communication and collaboration: A well-crafted business model is a guide for everyone in the company. It simplifies communication with stakeholders, team members, partners, and investors.
- Risk mitigation: A solid business model helps you identify potential risks and pitfalls. That means you can plan accordingly and implement strategies to mitigate risks.
- Resource allocation: A business model also helps you allocate resources effectively, and prioritize key activities that provide the most value.
- Attracting investors: Investors and partners luse the business model to evaluate the potential of your business. Having a solid business model will instil more confidence in your potential investors and partners.

How to set up a business model canvas
The business model canvas is a strategic management tool that helps you develop a good business models. The canvas is set up as a visual chart that shows your business’ value proposition, your proposed infrastructure, the customer segment you want to acquire, and how you’re going to finance your business.
The canvas was first created by Alexander Osterwalder and consists of nine building blocks that summarizes your business in one page:
- Customer segments
- Value propositions
- Channels
- Customer relationship
- Revenue streams
- Key resources
- Key activities
- Key partnerships
- Costs structure
The simple layout makes it perfect for sharing your idea with others without having to create an extensive pitch or sifting through lots of papers.
This is an example of a business model made using the business model canvas:
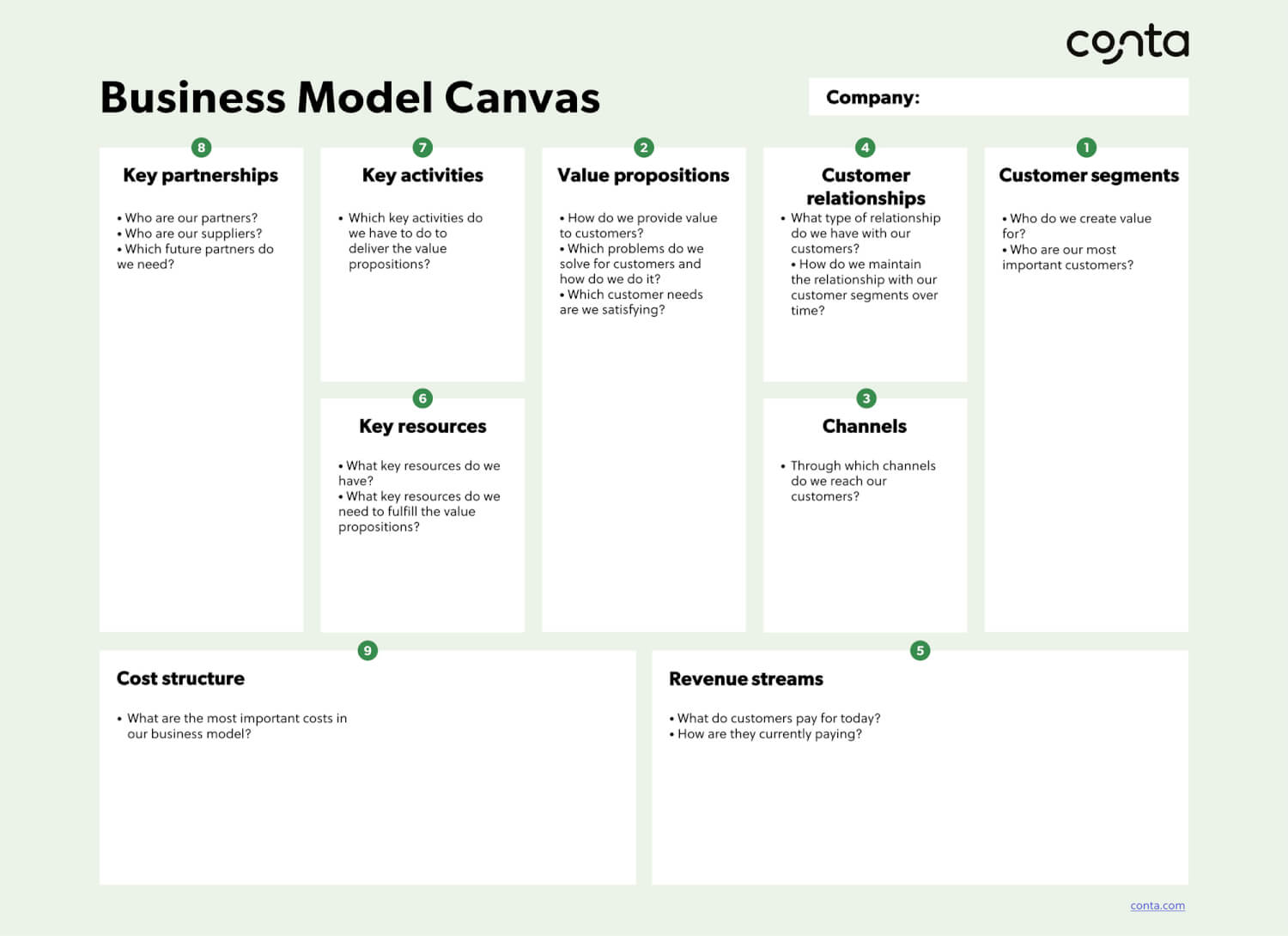
Want to try it for yourself? Download the free business model template.
A business model is always changing
Nothing is set in stone, not even your business model. Yes, it captures your initial ideas and plans, but as your business grows and your goals shift, your business model should evolve too. In fact, it’s a good idea to set aside time to review and update it regularly.
The aim isn’t to create a business model that will last for the next five or ten years, but to reflect the current situation of your business.
How to make a business model
1. Customer segments: Who are your customers?
A business idea often begins with a solution to a common problem or a way to make a task easier. It’s essentially about creating value for your customers.
Consider who you’re creating value for. You could have many potential customers, but it’s helpful to narrow it down by identifying your most important customer segments:
- Who are they?
- What are their needs?
It’s a good idea to have a brainstorming sessions or a workshop to come up with some ideas and create buyer personas. A buyer persona is a fictional person who represents a segment of your target audience. It should be based on research and knowledge about your target audience demographics, behaviour patterns, motivations, and goals.
You can get this knowledge by conducting focus groups, user interviews, surveys, and more. If you don’t know how to do that, you can hire a consulting firm to help you out—there are also articles and videos online covering this subject in detail.
See also: 10 things to do before starting a business
2. Value propositions: How does your business provide value to customers?
The second part of the business model covers how you plan to create value for your target audience. Answer these questions:
- How do we provide value to customers?
- Which problems do we solve for customers and how do we do it?
- Which customer needs are we satisfying?
These first two sections—customer segments and value propositions—form the core of your business model and lay the foundation for the other sections.
3. Channels: Where do you reach your customers?
Once you know who your customers are and how your business can create value for them, you need to figure out how to reach them. How will they learn about the products or services you’re offering?
There are a lot of options, so it’s important to consider the target audience you identified earlier. For example, if your target audience consists of retirees, platforms like TikTok or Instagram might not be the best channels to reach them. If you’re planning to sell clothes, consider whether you’re going to do it in a store or online, or both.
Additionally, think about how you’re going to deliver your products or services. For instance, an electrician has to be where the client is to deliver the service, while a graphic designer can send their work via email or share it online.
4. Customer relationships: How do you interact with customers?
In this section, explain how you’re going to interact with your customers and maintain good relationships with them. Decide whether you’ll offer personalized service, self-service, or a mix of both.
What you choose, depends a lot on the type of product or service you’re selling. For example, a grocery store can function well with self-service, while a hair salon requires personal service. Also, consider how you’ll encourage repeat purchases, if that’s your aim.
See also: Customer service tips for small businesses

5. Revenue streams: How does your business make money?
You might have noticed it already: Everything on the right side of the business model canvas are things that create revenue, while the left side covers your costs.
In this section you should answer these questions:
- What is the customer paying for when they buy from your company? Is it a one-time product, service, subscription, rental, or something else?
- How do you accept payment? Is it cash or card, invoice payments, bank transfers or something else?
It’s super important to have a clear path towards making money and ensuring a steady—and ideally growing—revenue stream.
6. Key resources: What resources do you have and how should they be used?
The next point you have to consider is what resources you need. This depends on what you’re selling, who your customers are, and what your value proposition is.
Resources can be anything that helps you deliver on your value proposition, from knowledge and expertise to physical materials. It could be anything from a company vehicle that you use to deliver goods, to marketing expertise that you have to hire. Another example of an important resource, could be a website that lets people book your services, or order your goods.
If you want to start a retail business, for example, your key resources include inventory, an inventory management system, a physical location, and employees.
7. Key activities: What do you have to do to add value to the company?
Key activities are the things you need in order to add value to your products or services, in short, what do you have to be good at to get customers and keep customers happy?
If you sell goods, the key activity might be producing goods. If you sell services, it could be performing those services. Key activities often include marketing and logistics as well. How are you going to get eyeballs on your products? How are you going to ship goods? How are you going to close deals?
Once you’ve been operating for a while and need to update your business model, focus on how to make these key activities more efficient, or to swap out key activities that aren’t working for you.
8. Key partnerships: Who are your partners?
As an entrepreneur, it is difficult to run a successful business without good partners.
Partners can include everything from suppliers that you have a good relationship with, to repeat clients that are strong ambassadors of your brand. Another example is investors that contribute money and expertise. All these partners ensure that you have the necessary resources for success.
A great example of a good partnership is Red Bull and GoPro.
In 2012, Red Bull teamed up with GoPro to sponsor a record-breaking skydive, capturing the moment with a GoPro camera. This collaboration evolved into a long-term strategic partnership, which led to the Red Bull Rampage, where GoPro cameras captured athletes’ point-of-views. This successful partnership is founded on the two companies’ shared audience of adrenaline enthusiasts:
Another example of collaborations is the coffee company Bialetti teaming up with successful tv-shows like Stranger Things or Squid Game to create custom percolators:
9. Cost structure: What are the most important costs in the company?
You likely have some costs in mind already: you need resources like materials, an office space or store, supplies, and personnel. By identifying important costs, you can avoid surprises when the bills start coming in.
Running a successful business comes down to generating more revenue than costs, so you should know how much your costs amount to. Good cost management involves categorizing expenses into fixed costs, variable costs, operational costs, distribution costs, and customer acquisition costs.
You should also have a cash flow budget, which shows the flow of money into your business and out of your business. This ensures that you’re earning more than you’re spending, and that you have the money to cover your costs.
See also: How to set up a budget
Save money—send invoices for free
When you set up a business model canvas, you have to include key costs in your business. When you start a business, you might have to invest in customer relationship management software (CRM), design software and collaboration tools like Miro or Mural. However, one way to cut costs is to do your invoicing for free.
Forget about those paid options, try Conta and send invoices for free:
Hopefully this guide has helped you on your way to creating a business model. While a business model helps you plan and launch your new business, some companies need a more detailed plan for day-to-day operations. That’s what a business plan is for!